Problem
1. Supply and Demand Mismatch in Computing Power
We find ourselves on the cusp of an incredible technological era, characterized by constant changes driven by revolutions in Artificial Intelligence, Augmented and Virtual Reality, 3D Rendering, the Metaverse, and more. These technological innovations are rapidly reshaping our world, creating a future unlike anything we have seen before. At the heart of these transformations lies computing power, which is the core energy in the digital age.
Despite its importance, one main problem exists – supply and demand mismatch in computing power.

The race to technological revolutions, especially to AI, has created a thirst in demand for computing power so insatiable. The demand for AI chips is soaring with tech giants like Microsoft, Meta, Amazon, and Alphabet racing to build data centers to make generative AI services such as ChatGPT, Runway AI, and Gemini a reality. Additionally, numerous original equipment manufacturers, original design manufacturers, and a long list of customers in biology, health care, finance, AI development, and robotics industries are also clamoring for GPUs. From big techs to small startups to individuals, everyone is scrambling to secure enough GPUs.
On the other hand, the GPU supply is currently limited. Even NVIDIA, the leading GPU manufacturer in the estimated USD 65.27 Billion GPU market, is also facing supply constraints that CEO Jensen Huang had to discuss how ‘fairly’ they decide who can buy their GPU chips.
2. Underutilization of GPU Resources
Despite the mismatch in supply and demand, an important challenge is that GPUs are not being used to their full potential.
The majority of GPUs are concentrated in centralized providers. Typically, only 50% to 70% of their computing resources are actually utilized, leaving 30% constantly underutilized. Despite this unused capacity, there is always demand for it elsewhere. However, the high costs associated with these centralized models have created barriers for many users to access cloud computing services, preventing them from taking advantage of these computing resources.
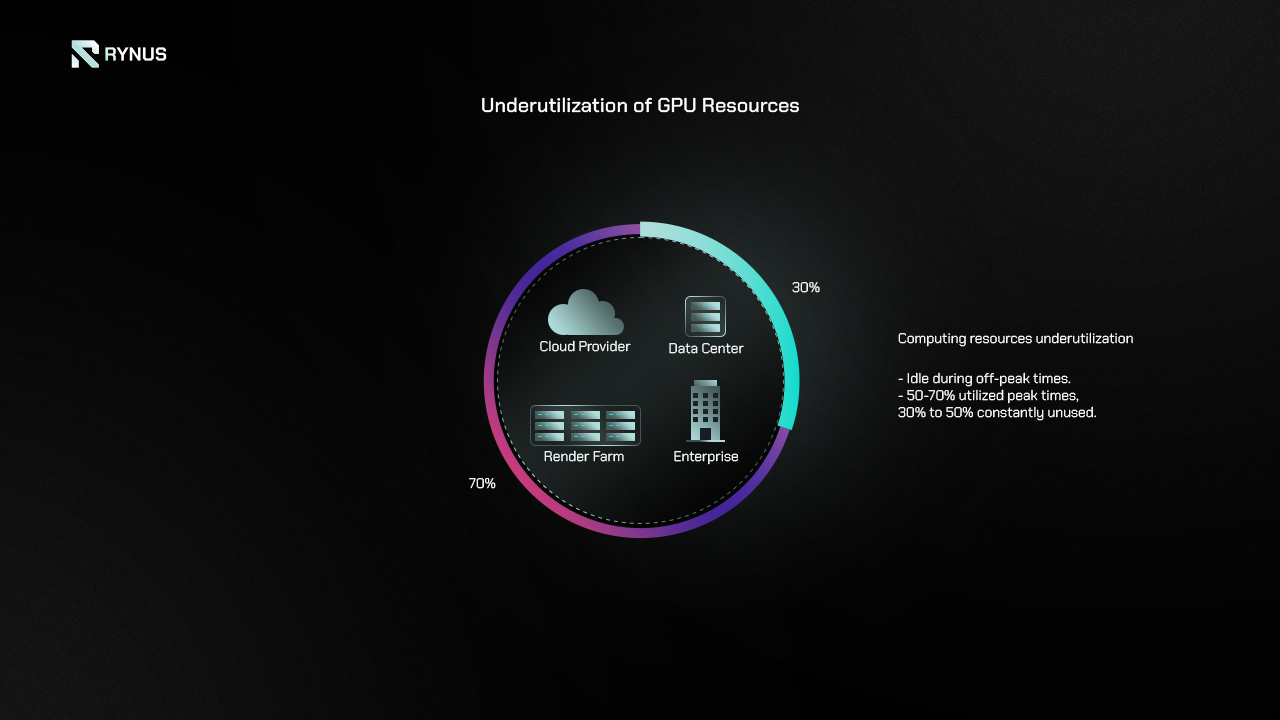
Furthermore, there are hundreds of millions of GPUs that have been sold to tech companies, enterprises, data centers, cryptocurrency mining companies, studios, and individuals, and are also sitting underutilized. Due to declining block rewards, GPUs purchased for cryptocurrency mining have become inefficient. Individuals or studios typically do not utilize their own computing resources throughout the day. Nevertheless, people worldwide still need to buy new devices to meet their computing needs.
This situation represents a significant paradox where available GPU computing potential is abundant, yet it remains largely untapped. Opening up access to these resources will be enough to significantly impact GPU resource supply.
3. High Cost
A few big corporations/companies mainly control the current centralized GPU cloud computing models. This has resulted in a market with limited competition and high service costs. The concentration of power in the hands of these corporations/companies has led to inflated pricing structures, which makes it difficult for smaller users to access cloud services.
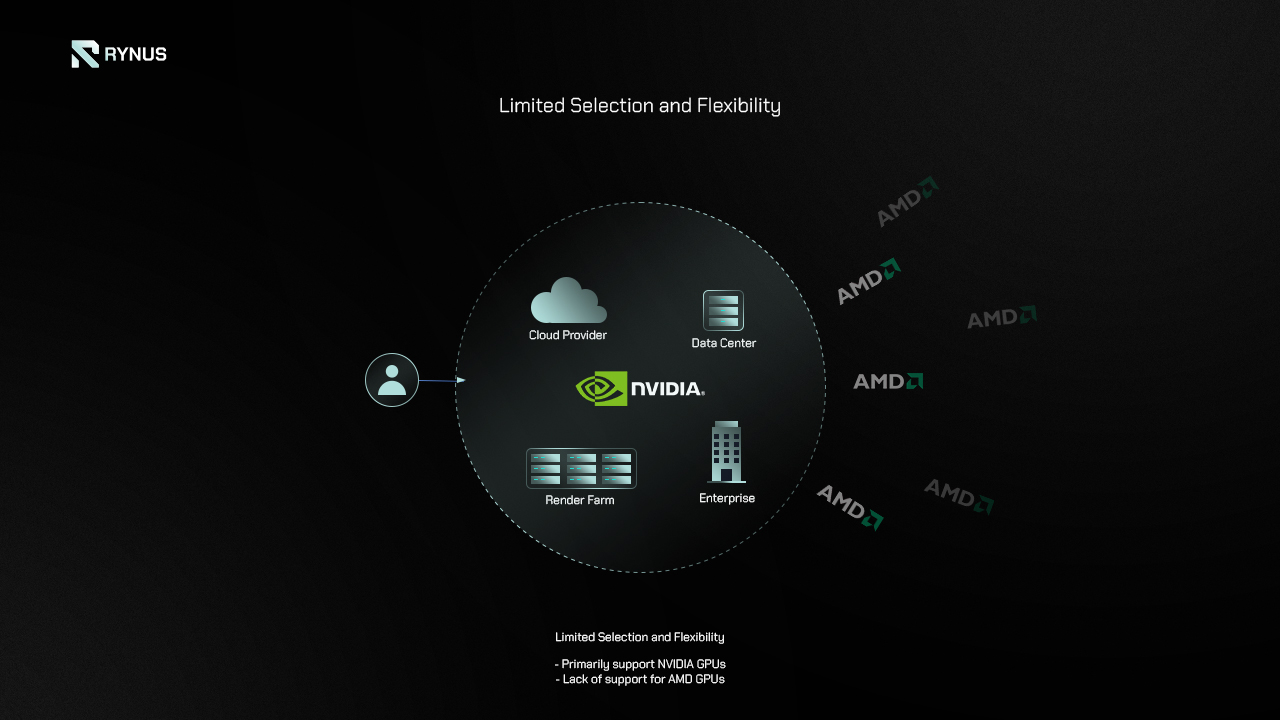
4. Limited Selection and Flexibility
The limited selection and inflexibility of GPU manufacturers and models available in centralized GPU cloud computing platforms is another significant issue. The majority of these platforms primarily support NVIDIA GPUs, neglecting the increasing training/rendering performance capabilities of AMD GPUs. This lack of support for AMD GPUs is noteworthy, considering its significant presence in the industry. Additionally, these platforms are constrained to standardized configurations, making it difficult for them to accommodate specialized accelerators or emerging new GPUs that are optimal for cutting-edge 3D rendering and AI pipelines.
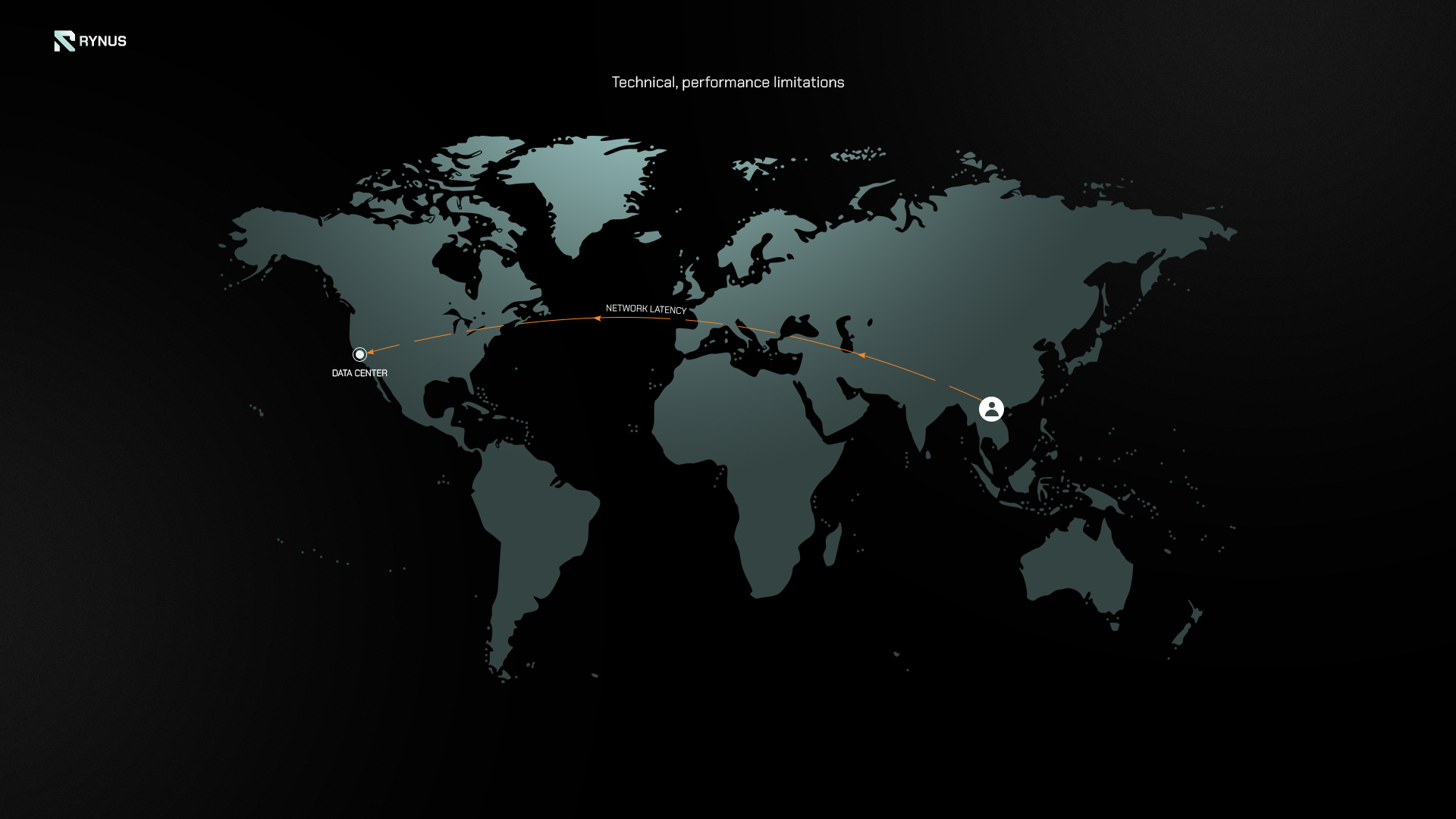
5. Technical and Performance Limitations
Centralized GPU cloud computing models present several issues that can impact performance for graphics workloads like 3D rendering and AI training. Concentrated GPU resources within large data centers introduce network latency when transferring data between remote GPU clusters and client applications. For real-time workflows relying on iterative access, this lag is problematic.
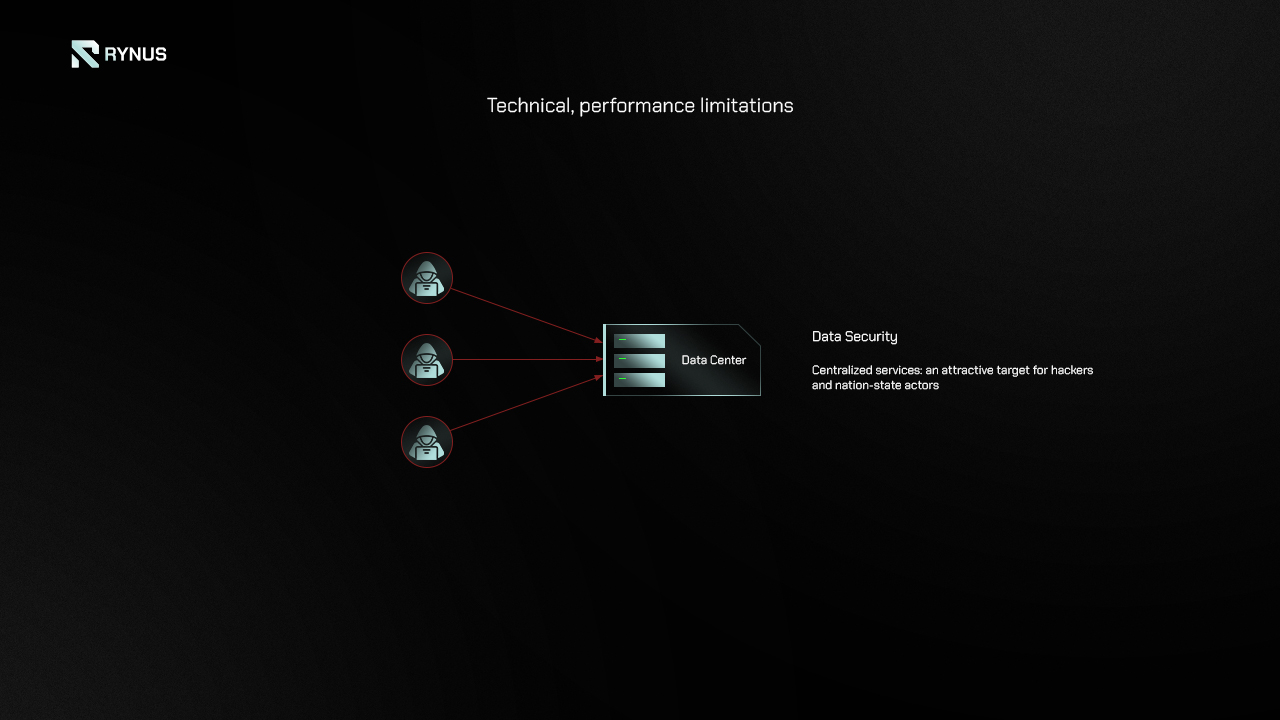
Another main issue with centralized GPU cloud computing models is data security. Storing and processing significant amounts of data in large data centers creates a single point of failure or attack surface. When all customer data and workloads are consolidated in one location under the control of a single entity, it becomes an attractive target for hackers and nation-state actors. The data, especially in creative fields like rendering or AI training, is highly sensitive and requires proper protection.
Solution
1. Democratizing Computing Power and Solving Supply-Demand Mismatch
We believe it is crucial to distribute the tremendous power of computing widely and ensure that everyone benefits from it, not just a select few. To achieve this, we aim to decentralize and democratize our immense computing power, making it truly accessible to everyone. We want every voice of intelligence, no matter how small, to be heard and for the secrets of technology to be unlocked for the benefit of all humanity.
Rynus democratizes computing power and radically solves the problem of supply and demand mismatch worldwide. Rynus is a decentralized cloud computing network, giving everyone access to abundant cloud computing power. We connect global computing resources, matching supply and demand at the right time to ensure that all computing resources are fully utilized and not wasted.
Rynus allows all the disadvantaged groups to take advantage of cheap cloud computing power from a decentralized model. We create a greener computing world, reducing environmental pollution by utilizing all computing power to the maximum extent. A more diverse world will be reshaped because, with Rynus, everyone’s creative ideas and design styles have access to diverse and affordable cloud computing power.
The nature of Rynus is decentralized cloud computing. We take the first step in the field of 3D rendering and AI training and solve all existing core problems by providing:
2. More Affordable and Transparency
Rynus’s decentralized GPU computing on blockchain model addresses the inequities of centralized cloud monopolies by creating a truly open and competitive marketplace. Individuals globally can contribute unused GPU resources, fostering vastly more competition than the current duopoly. With thousands of peer-to-peer nodes worldwide, no single entity can dictate pricing. This model benefits both underserved customers and independent suppliers by lowering barriers to participate affordably. Workloads also gain the flexibility to leverage the most competitive resources dynamically, and distributed ledgers promote transparency. By leveraging blockchain technology, Rynus dismantles centralized control over pricing, establishing an equitable system that encourages innovation and inclusion.
3. Unlimited Availability
By leveraging unlimited independent nodes globally with idle GPU resources, Rynus vastly increases the total available GPU computational power compared to centralized data centers. This model avoids the limitations of centralized data centers, such as bottlenecks and queues during peak periods, by dynamically scheduling workloads across a globally shared pool of resources. With a peer-to-peer architecture, tasks can be routed to hardware with available resources anywhere in the world, resulting in consistent throughput without competition for limited resources or reduced speeds that can occur on centralized platforms.
4. Diverse Selection and Flexibility
Rynus aims to address the current limitations and lack of flexibility in accessing GPU resources within centralized GPU cloud models. Unlike centralized models, our platform supports a wide range of GPU manufacturers, including NVIDIA, AMD, Apple, and Intel. By creating an open and decentralized marketplace for graphics hardware, we allow individuals and entities to contribute their hardware resources to a decentralized cloud ecosystem. This provides users with the flexibility to choose from various GPU manufacturers and models, driving innovation in rendering and deep learning through specialized computing power that are not available in traditional centralized platforms. Furthermore, we are actively working on the development of a dedicated multi-GPU rendering engine that will support NVIDIA and AMD GPUs for 3D rendering. As part of our plans, we intend to create an enhancement plugin for TensorFlow that will support both AMD and NVIDIA, further expanding the capabilities of our platform.
5. Reduced Latency and Improved Security
By distributing GPU resources across many independent nodes worldwide, workloads can be routed to hardware placed closer to end users, avoiding long-distance data transfers over centralized cloud networks. This significantly reduces latency. Based on blockchain technology, Rynus maintains users’ full ownership and control over their data, models, and intellectual property.
6. Democratizing Access to Unlimited GPU Resources for Mutual Gain
Rynus is a game-changer in the field of cloud computing. We address the issue of underutilization of GPU resources and provide a solution that benefits everyone involved.
The decentralized nature of our platform allows users to contribute their own GPU resources to the system, which can be used by others in need of additional resources. This not only helps to reduce the gap between supply and demand, but it also provides an opportunity for those with free GPU resources to monetize by contributing their resources to the system.
3D rendering and AI training users can access unlimited GPU computing resources that are abundant and difficult to access on any platform to serve the most complex and large-scale rendering and model training tasks.
7. Establishing a Democratic, Fair, and Free Cloud Computing Market
GPU/CPU providers (Workers) participating in the Rynus network will bid for computing jobs. Unlike other cloud computing services where the service provider or the platform sets the prices, the rental cost of GPU/CPU for a computing job on Rynus is determined by the Workers themselves.
This pricing is influenced by supply and demand dynamics within the cloud computing market at that particular time. As a result, the cost fluctuates based on real-time market conditions, ensuring a more equitable and transparent pricing model. This approach empowers Workers to have control over their pricing, fostering a decentralized ecosystem where market forces dictate prices. By doing so, Rynus promotes a cloud computing market that is not only more democratic and fair but also offers greater freedom, aligning with the principles of a decentralized and user-driven network.
8. Green Initiatives, Carbon Reduction, and Environmental Sustainability
Rynus is a decentralized GPU cloud computing platform built on blockchain technology, committed to promoting environmental sustainability and reducing carbon emissions. By leveraging a green blockchain, Rynus ensures that the energy used by its network is directed towards providing valuable computing power, avoiding the wasteful energy consumption typical of traditional proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains. This is achieved through its innovative proof-of-compute consensus algorithm, which focuses on the completion of computing jobs.
2 key ways Rynus reduces carbon emissions:
1. Efficient use of underutilized GPU resources.
Rynus connects underutilized GPUs globally, maximizing their use for processing computing jobs. This approach not only alleviates the shortage of computational resources but also reduces the need for new hardware production. By utilizing existing resources more effectively, Rynus significantly cuts down on the energy required for manufacturing new GPUs and other hardware.
2. Reduction in the need for new hardware manufacturing.
Rynus’s strategy of not building new data centers or purchasing new hardware results in substantial environmental benefits. This includes reducing carbon emissions during the manufacturing process and minimizing electronic waste.
Moreover, centralized data centers are known for their high energy consumption and significant carbon footprint. Rynus’s decentralized model addresses these concerns by distributing computational tasks across individual and idle GPUs. This reduces the reliance on large data centers, leading to lower overall energy consumption and a reduced environmental impact.
By adopting these green initiatives, Rynus not only supports the efficient use of resources but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainability in the tech industry.