What is the Sentry Node?
The Sentry Node is a crucial component of the Rynus Network, dedicated to ensuring the integrity and performance of Workers. By verifying the specifications provided by Workers, the Sentry Node upholds the network’s Quality of Service standards.
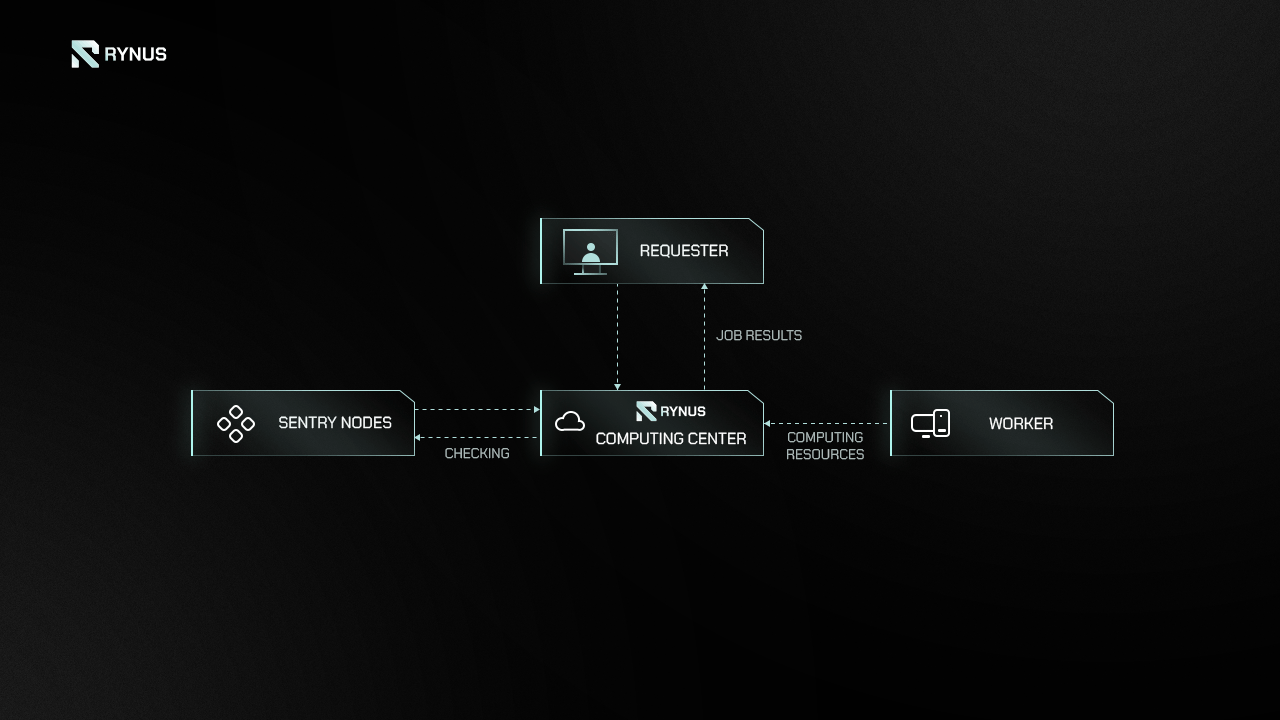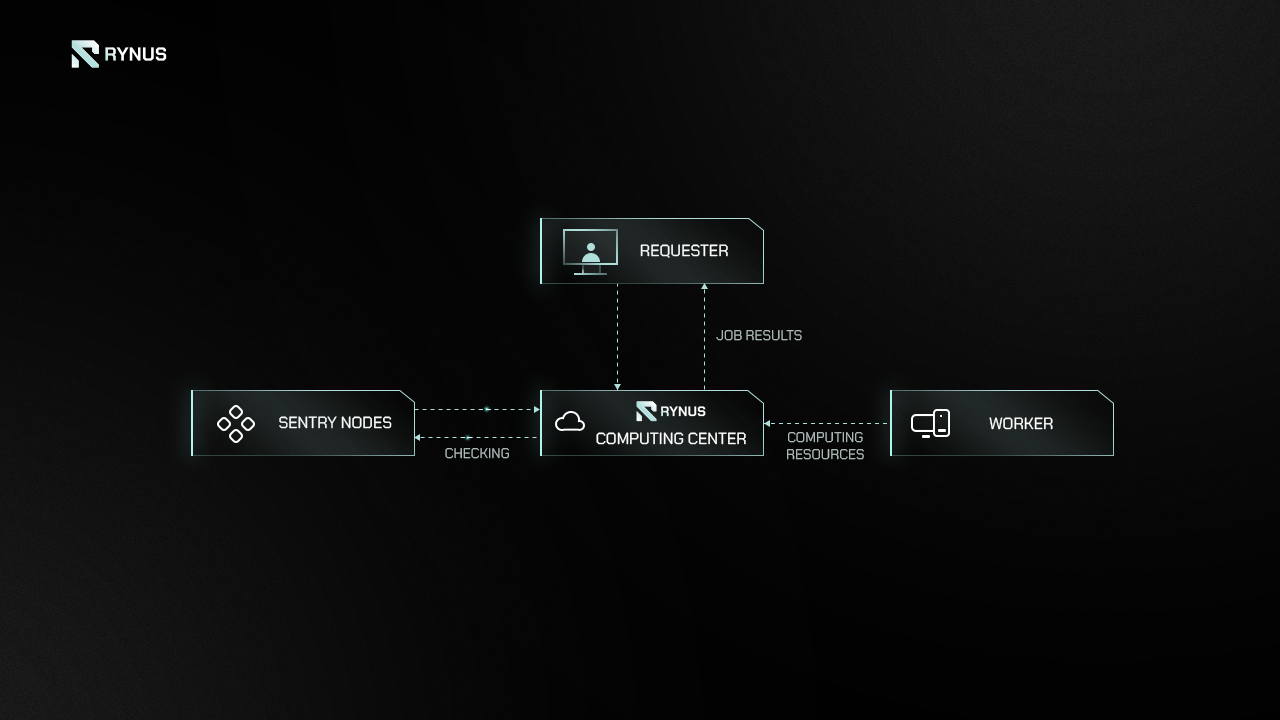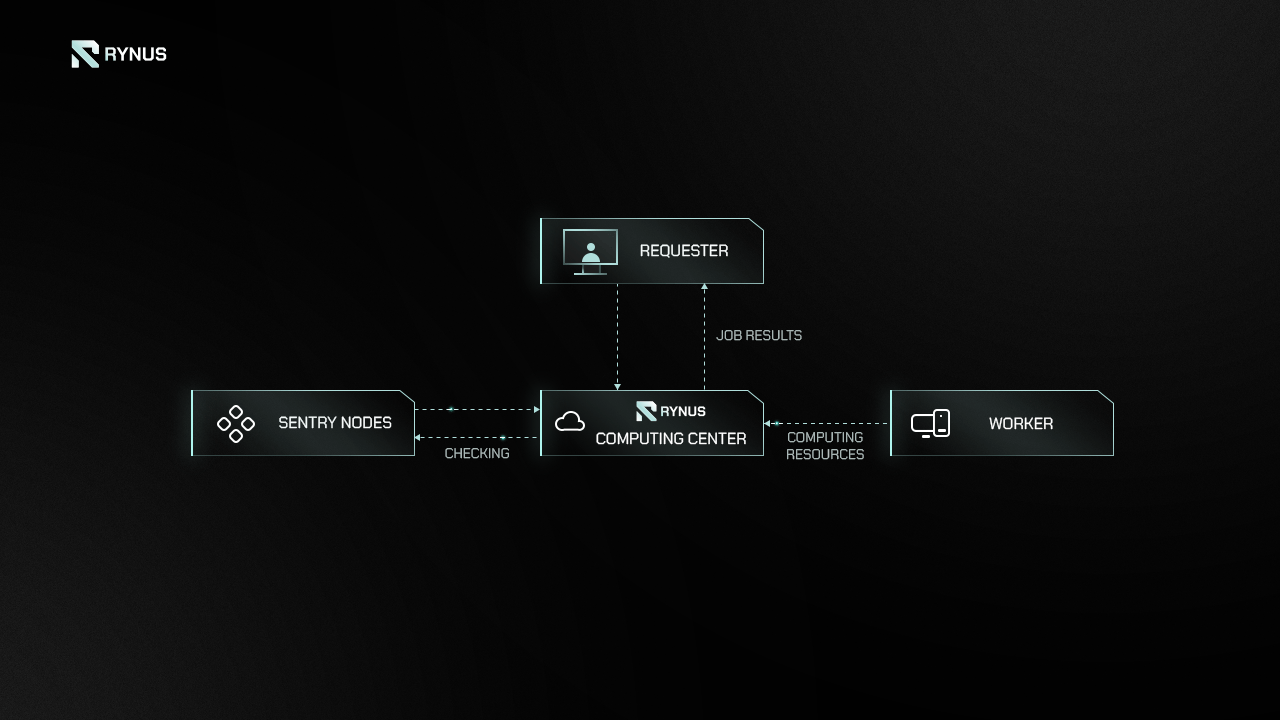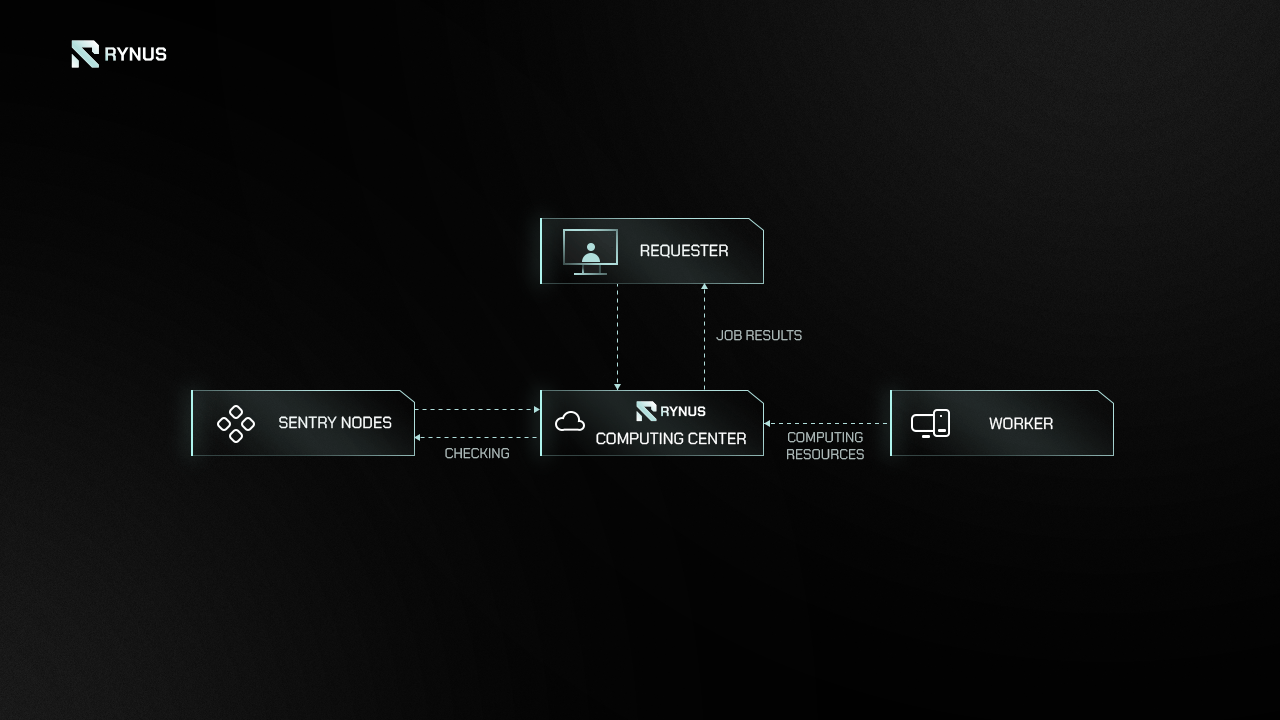
1. Check Processes
- When a Worker joins the Rynus Network, the Sentry Node validates the Worker’s specifications to determine eligibility for network participation.
- The Sentry Node conducts random checks on Workers in standby mode to ensure ongoing compliance with network standards.
- During the computing state, the Sentry Node collects and assesses service information to evaluate the actual performance and service status of the Workers.
2. Outcome of Checks
- The Sentry Node confirms the accuracy of Worker specifications and successful registration.
- It influences the scheduling opportunities and priorities of Workers by the AI Core based on their performance and reliability.
- The Sentry Node determines penalties for Workers that fail to meet service quality standards.
3. Checking Methods
- Performance Parameters: The Sentry Node directly reads and analyzes the Worker’s performance data.
- Simulation Testing: Acts as a Requester to test applications and interactions, ensuring compliance with the claimed specifications.
Who can run Sentry Nodes?
Anyone can operate a Sentry Node by obtaining a Sentry Node License (NFT) or receiving delegation from the License owner. The license allows you to earn rewards by running the Sentry Node Application, either on your own machine or by delegating it to another user’s machine.
Licenses can be purchased from checker.rynus.io or through secondary markets in the future. Stay tuned for contract releases and further updates.
How do Sentry Nodes work?
Sentry Nodes play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and service quality of the Rynus Network by rigorously checking Worker nodes and their service processes. The primary parameters they monitor include Liveness, Capacity, and Quality of Service. The methods used for these checks involve heartbeat collection, benchmark testing, and link data collection and analysis.
Sentry Node Operation
Sentry Nodes are tasked with monitoring specific Workers and must complete various check tasks across all task types:
- Liveness: Continuously detect Worker heartbeat, conducted every minute.
- Quality of Service: Check Worker computing quality, performed every minute during active computing.
- Capacity: Daily assess the Worker’s capacity and specifications.
If a Sentry Node fails to respond within the expected time frame, the check task is reassigned to another Sentry Node. If a Sentry Node goes offline, all its tasks are reassigned. In cases where a Capacity Check has been completed by the previous Sentry Node, the results are voided, and the newly assigned Sentry Node must perform the Capacity Check again.
Slashing
To maintain high standards, Rynus Network enforces strict penalties for Sentry Nodes that fail to perform accurately:
- Two or More Incorrect Calculations in a Week: The Sentry Node is banned from earning rewards for a month, and no tasks will be assigned during this period.
- Five or More Incorrect Calculations in a Month: The Sentry Node is banned from earning rewards for six months, and no tasks will be assigned during this period.
- Accumulated Ten Incorrect Calculations: The Sentry Node is permanently banned and disqualified from serving as a Sentry Node.
Sentry Node Status
Sentry Nodes can exist in one of five statuses, each indicating their operational state. These statuses are essential for effective management and troubleshooting within the Rynus Network:
- Checking: Actively performing verification tasks.
- Ready: Prepared to receive new tasks but not currently engaged in checking.
- Offline: Not operational due to network issues or maintenance.
- Banned: Disqualified from earning rewards due to repeated failures or policy violations.
- Pending: Awaiting approval for delegation.